The Importance of Eye Exams for Children: Protecting Their Vision

Regular eye exams are crucial for children as they help detect and correct vision problems early, ensuring optimal development and academic success.
Ensuring your child’s healthy development involves many facets, and one that’s often overlooked is the importance of regular eye exams. Just as you schedule routine check-ups with your pediatrician, incorporating eye exams into your child’s healthcare routine can make a significant difference in their overall well-being. Let’s delve into the importance of regular eye exams for children: protecting their vision from an early age.
Why Are Eye Exams Important for Children?
Eye exams for children are vastly important because a child’s vision can change rapidly, and many vision problems don’t have obvious symptoms. Early detection and treatment can prevent vision issues from affecting a child’s learning, development, and overall quality of life.
Detecting Vision Problems Early
Many children don’t realize they have a vision problem because they’ve never experienced clear vision. Undetected vision problems can lead to difficulties in school, sports, and other activities. Regular eye exams can catch these issues early.
Preventing Learning Difficulties
Good vision is essential for learning. Children with uncorrected vision problems may struggle with reading, writing, and other academic tasks. By addressing vision issues, you can help your child succeed in school.

Here are some reasons why regular eye exams are important:
- Early Detection: Identifies problems like amblyopia (lazy eye) and strabismus (crossed eyes) early on.
- Academic Performance: Ensures clear vision for reading and writing, crucial for school success.
- Overall Development: Supports proper visual development, affecting motor skills and coordination.
Regular eye exams help ensure children have the vision they need to succeed in all areas of life.
When Should Children Have Their First Eye Exam?
The timing of a child’s first eye exam is crucial. Most experts recommend that children have their first comprehensive eye exam by age 3, or earlier if there’s a family history of eye problems or if any signs of vision issues are present.
Infant Eye Exams
Even before age 3, infants should have their eyes examined by their pediatrician. These early screenings can identify any major concerns that need immediate attention. More in-depth exams are usually reserved for older toddlers and children.
Preschool Eye Exams
Once your child reaches preschool age, a comprehensive eye exam is a must. At this age, optometrists can use a range of tests to assess vision, eye alignment, and overall eye health. Many vision problems don’t show obvious symptoms, so a professional exam is essential.
Some key milestones for eye exams include:
- Infancy: Pediatrician screens for basic eye health.
- 3 Years Old: Comprehensive eye exam by an optometrist or ophthalmologist.
- School-Age: Regular exams every 1-2 years, or as recommended by the eye doctor.
Following these milestones ensures that any potential vision problems are caught and managed promptly.
What Happens During a Children’s Eye Exam?
Knowing what to expect during an eye exam can help ease any anxiety your child may have. A typical children’s eye exam involves a series of tests to assess various aspects of vision and eye health.
Visual Acuity Tests
Visual acuity tests measure how well your child can see at different distances. This usually involves reading letters or looking at pictures on an eye chart. These tests help determine if your child needs glasses or contacts.
Eye Alignment Tests
Eye alignment tests check how well your child’s eyes work together. These tests can detect problems like strabismus, where the eyes don’t align properly. Early detection and treatment of strabismus can prevent long-term vision problems.
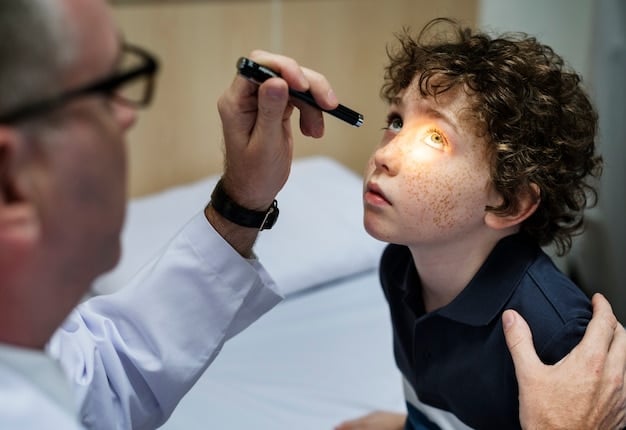
Here is a list of the tests typically performed:
- Visual Acuity: Measures clarity of vision at different distances.
- Eye Alignment: Checks how well the eyes work together.
- Refraction: Determines the need for corrective lenses.
- Eye Health: Examines the overall health of the eyes.
Each test plays a crucial role in constructing a complete picture of your child’s visual health.
Common Vision Problems in Children
Children can experience various vision problems, some of which are more common than others. Understanding these common issues can help you recognize potential symptoms and seek timely treatment.
Refractive Errors
Refractive errors, such as nearsightedness (myopia), farsightedness (hyperopia), and astigmatism, are common in children. These issues can be corrected with glasses or contacts, allowing your child to see clearly.
Amblyopia (Lazy Eye)
Amblyopia, or lazy eye, occurs when one eye doesn’t develop normal vision. Early detection and treatment, such as patching the stronger eye, can improve vision in the weaker eye. If left untreated, amblyopia can lead to permanent vision loss.
Some common vision issues include:
- Myopia (Nearsightedness): Difficulty seeing distant objects clearly.
- Hyperopia (Farsightedness): Difficulty seeing close objects clearly.
- Astigmatism: Blurred vision due to an irregularly shaped cornea.
- Amblyopia (Lazy Eye): Reduced vision in one eye.
Recognizing these common problems is the first step toward ensuring your child gets the treatment they need.
How to Prepare Your Child for an Eye Exam
Preparing your child for an eye exam can help make the experience more positive and productive. Start by explaining what will happen during the exam in a simple, age-appropriate way.
Talk About the Eye Doctor
Explain that the eye doctor is a friendly helper who wants to make sure their eyes are healthy. You can even practice looking at an eye chart together at home to familiarize your child with the process.
Bring Comfort Items
If your child is anxious, consider bringing a favorite toy or blanket to the appointment. This can provide comfort and help them feel more secure during the exam. Make sure they are well-rested and fed, too.
Consider the following tips to help prepare your child:
- Explain the Process: Describe what will happen in a way they understand.
- Practice at Home: Familiarize them with eye charts and simple vision tests.
- Stay Positive: Maintain a calm and reassuring attitude.
With preparation, your child’s appointment is more likely to be handled smoothly.
The Role of Nutrition in Children’s Eye Health
Good nutrition plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy eyes for children. A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can support optimal vision and prevent certain eye problems.
Key Nutrients for Eye Health
Vitamins A, C, and E, as well as zinc and omega-3 fatty acids, are essential for eye health. These nutrients can be found in a variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, and fish. Encourage your child to eat a colorful and diverse diet to support their vision.
Foods to Include in Your Child’s Diet
Include foods like carrots, spinach, sweet potatoes, citrus fruits, and salmon in your child’s diet. These foods are packed with nutrients that can help protect their eyes from damage and promote healthy vision.
Some dietary additions to promote healthy vision include:
- Vitamin A: Found in carrots, sweet potatoes, and leafy greens.
- Vitamin C: Abundant in citrus fruits, berries, and bell peppers.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish like salmon and flaxseeds.
Ensure your child gets a variety of nutrient-rich foods to support their eye health.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 👀 Importance of Eye Exams | Ensures early detection and prevention of vision issues that can affect learning. |
| 📅 When to Start | First comprehensive exam by age 3, or earlier with risk factors. |
| 🍎 Nutrition for Eyes | Nutrients like Vitamin A, C, E, and Omega-3 support good eyesight. |
| 🤝 Preparing Your Child | Explain the process, practice at home, and bring comfort items for a positive experience. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
▼
Regular eye exams are vital for detecting and correcting vision problems early, ensuring optimal learning and development. Undetected vision issues can affect school performance and social interactions.
▼
Children should have their first comprehensive eye exam by age 3. Infants should have basic screenings by their pediatrician. Early detection is key to addressing problems effectively.
▼
A typical exam includes visual acuity tests, eye alignment checks, and refraction assessments. The optometrist evaluates overall eye health and determines if corrective lenses are needed for clear sight.
▼
Common problems include nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism, and amblyopia (lazy eye). Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes and prevent long-term visual impairment.
▼
Explain the process, practice at home with basic eye tests, and bring comfort items. Staying positive and reassuring can help ease anxiety and make the experience pleasant.
Conclusion
In conclusion, prioritizing regular eye exams for children is an investment in their future. Early detection and treatment of vision problems can significantly impact their learning, development, and overall quality of life.





